Print MATLAB Source Code in LaTeX
Method 1: by the listings package12 (the lstlisting environment with the language option)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{listings}
\begin{document}
\begin{lstlisting}[language=matlab]
%% Sample Matlab code
A = [1, 2, 3;... foo
4, 5, 6];
s = 'abcd';
for k = 1:4
disp(s(k)) % bar
end
% create row vector x, then reverse it
x = linspace(0,1,101);
y = x(end:-1:1);
\end{lstlisting}
\end{document}

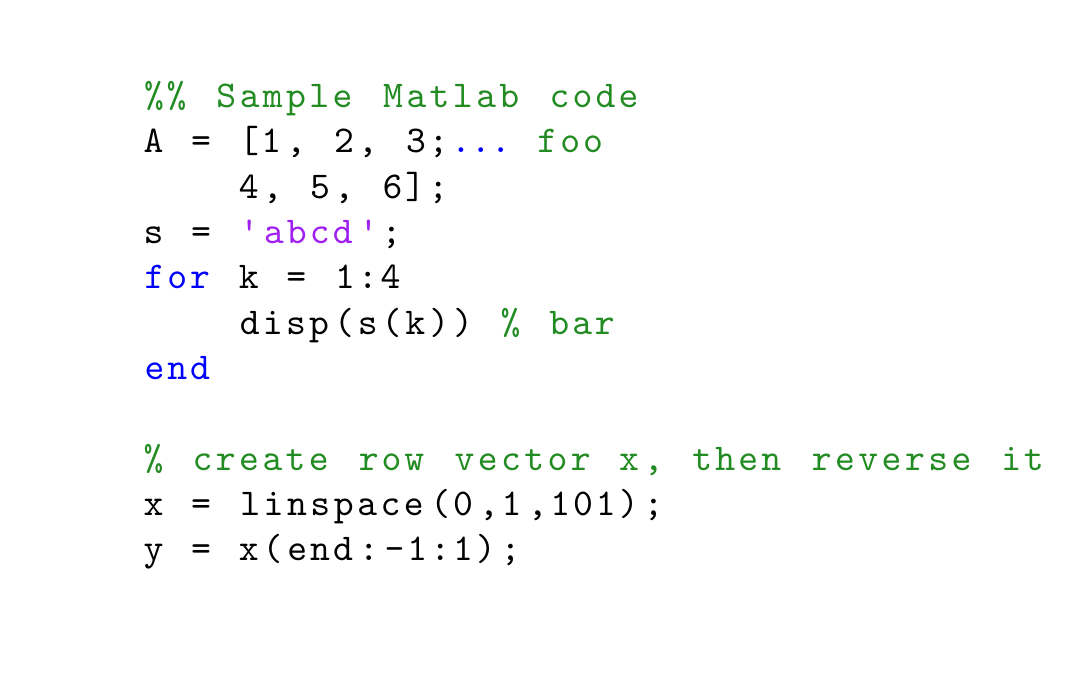
Method 2: by the matlab-prettifier package3 (the lstlisting environment with the style option, where at this time we don’t need to import the listings package)
(a) style=Matlab-editor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{matlab-prettifier}
\begin{document}
\begin{lstlisting}[style=Matlab-editor]
%% Sample Matlab code
A = [1, 2, 3;... foo
4, 5, 6];
s = 'abcd';
for k = 1:4
disp(s(k)) % bar
end
% create row vector x, then reverse it
x = linspace(0,1,101);
y = x(end:-1:1);
\end{lstlisting}
\end{document}
(b) style=Matlab-bw
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{matlab-prettifier}
\begin{document}
\begin{lstlisting}[style=Matlab-bw]
%% Sample Matlab code
A = [1, 2, 3;... foo
4, 5, 6];
s = 'abcd';
for k = 1:4
disp(s(k)) % bar
end
% create row vector x, then reverse it
x = linspace(0,1,101);
y = x(end:-1:1);
\end{lstlisting}
\end{document}

(c) style=Matlab-Pyglike
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{matlab-prettifier}
\begin{document}
\begin{lstlisting}[style=Matlab-Pyglike]
%% Sample Matlab code
A = [1, 2, 3;... foo
4, 5, 6];
s = 'abcd';
for k = 1:4
disp(s(k)) % bar
end
% create row vector x, then reverse it
x = linspace(0,1,101);
y = x(end:-1:1);
\end{lstlisting}
\end{document}

(d) By combining other options4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{matlab-prettifier}
\begin{document}
\begin{lstlisting}[frame=single,
numbers=left,
style=Matlab-Pyglike]
%% Sample Matlab code
A = [1, 2, 3;... foo
4, 5, 6];
s = 'abcd';
for k = 1:4
disp(s(k)) % bar
end
% create row vector x, then reverse it
x = linspace(0,1,101);
y = x(end:-1:1);
\end{lstlisting}
\end{document}

What’s more, we can directly print the source code from an external .m script file4:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{matlab-prettifier}
\begin{document}
\lstinputlisting[
frame=single,
numbers=left,
style=Matlab-editor
]{script.m}
\end{document}

Besides, the documentation of matlab-prettifier package provides more customization options3.
Method 3: use the listings package to customize styles
We can use the listings package to customize styles by a set of properties. Here is an example from the article1, although it is originally designed for the programming language Octave.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{listings}
\usepackage{xcolor}
\definecolor{codegreen}{rgb}{0,0.6,0}
\definecolor{codegray}{rgb}{0.5,0.5,0.5}
\definecolor{codepurple}{rgb}{0.58,0,0.82}
\definecolor{backcolour}{rgb}{0.95,0.95,0.92}
\lstdefinestyle{mystyle}{
backgroundcolor=\color{backcolour},
commentstyle=\color{codegreen},
keywordstyle=\color{magenta},
numberstyle=\tiny\color{codegray},
stringstyle=\color{codepurple},
basicstyle=\ttfamily\footnotesize,
breakatwhitespace=false,
breaklines=true,
captionpos=b,
keepspaces=true,
numbers=left,
numbersep=5pt,
showspaces=false,
showstringspaces=false,
showtabs=false,
tabsize=2
}
%\lstset{style=mystyle}
\begin{document}
\lstinputlisting[language=Matlab,style=mystyle]{script.m}
\end{document}

More properties can be found in the documentation of listings package2.
References